Have you ever noticed that different parts of your tongue taste different flavors? It’s not just your imagination, it’s actually true. Each part of your tongue has receptors that detect different tastes. In this article, we will explore the different parts of the tongue and how they work.
The Five Basic Tastes
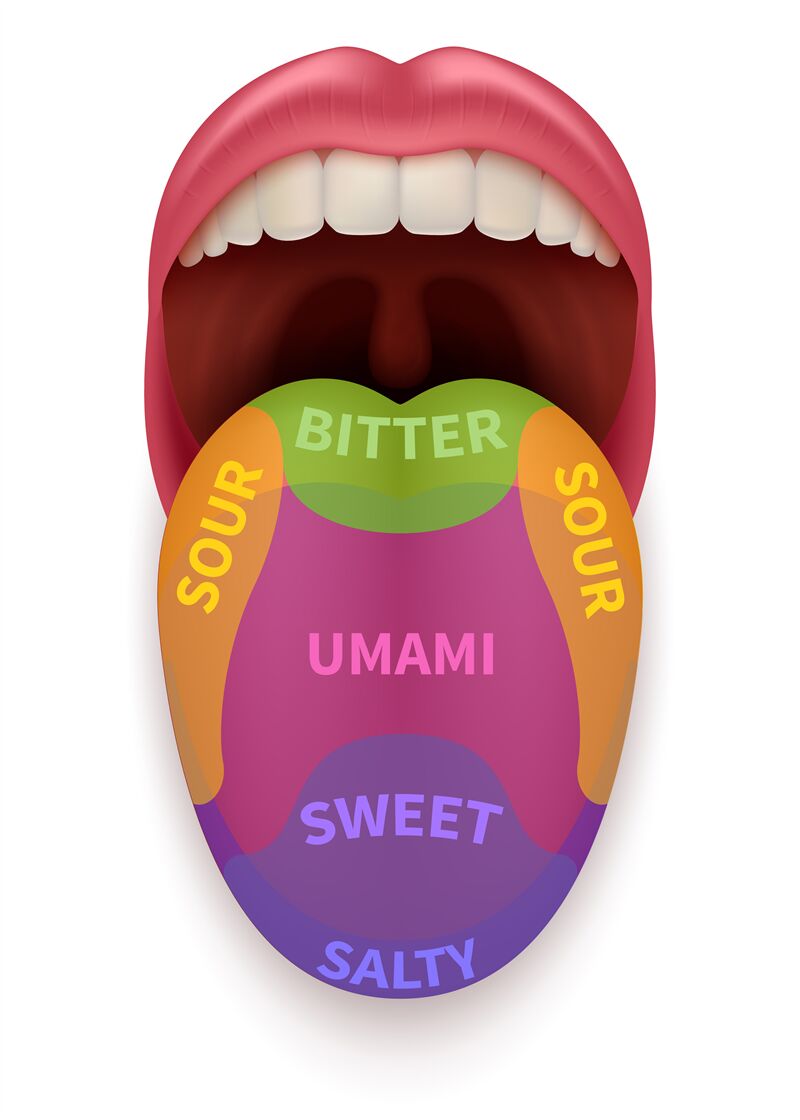
Before we dive into the different parts of the tongue, let’s review the five basic tastes that humans can detect. These are sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami. Sweetness is associated with sugar, while saltiness is associated with sodium. Sourness is associated with acidic foods, bitterness is associated with alkaloids, and umami is associated with savory foods.
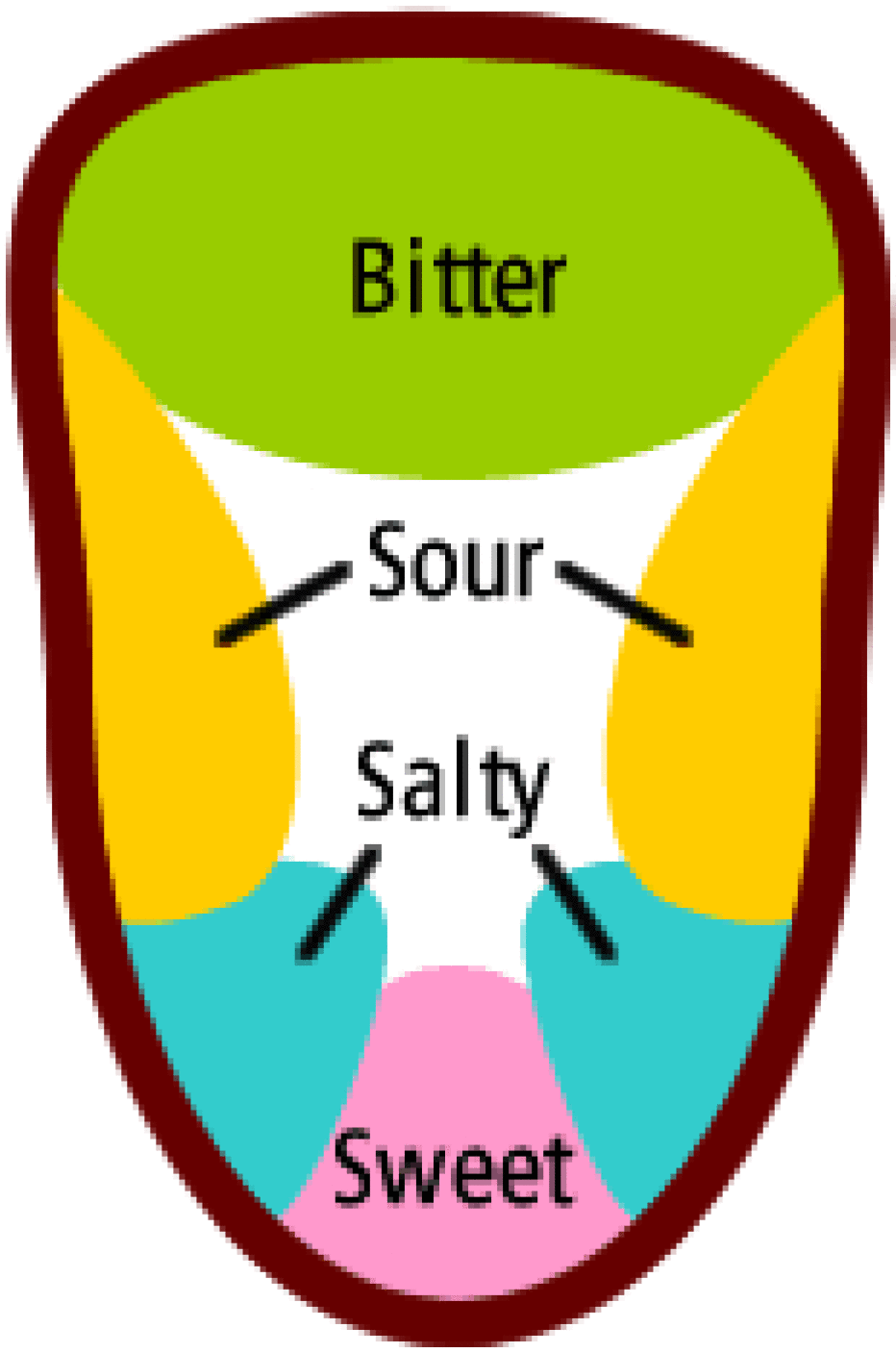
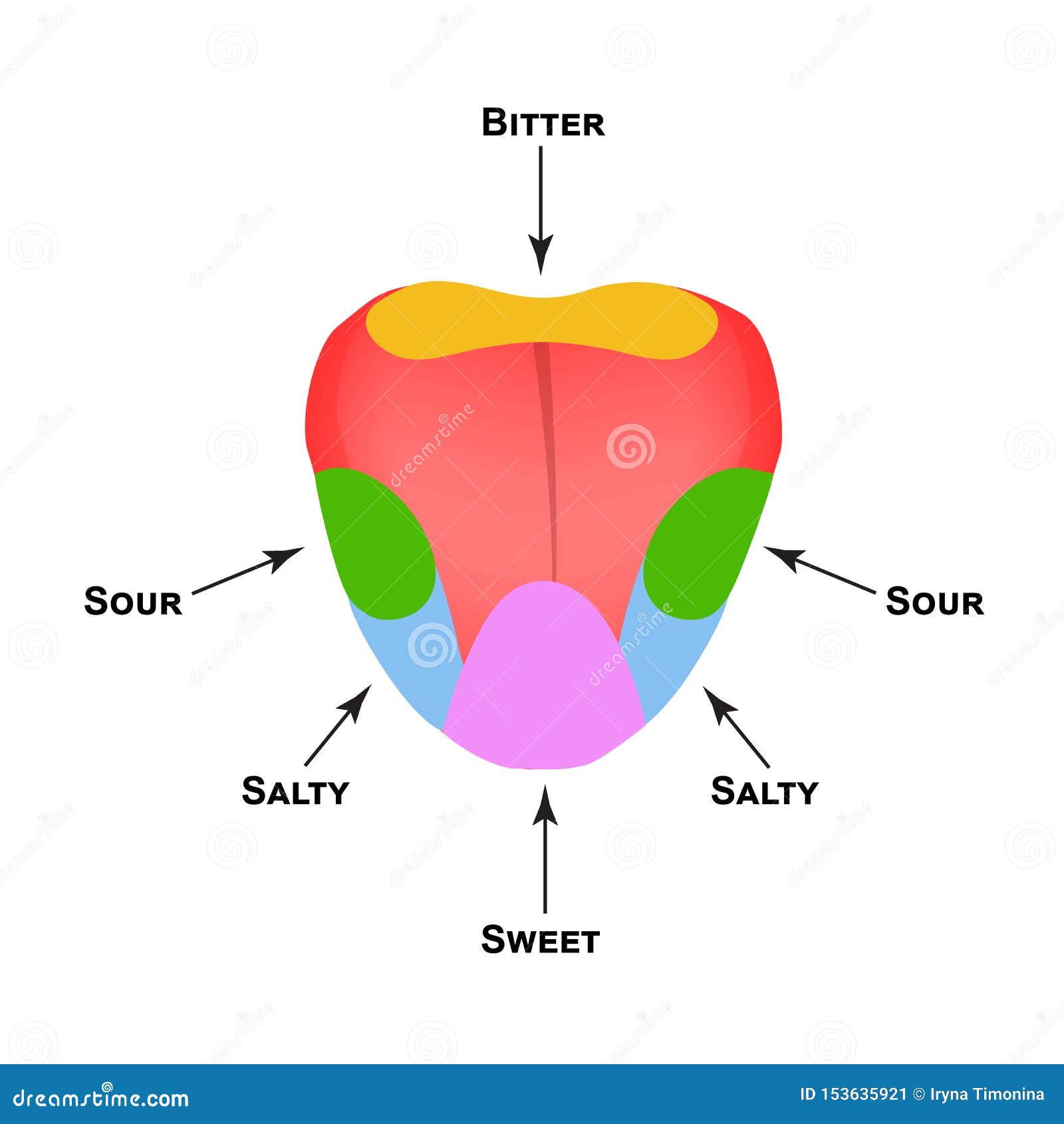
The Tongue Map
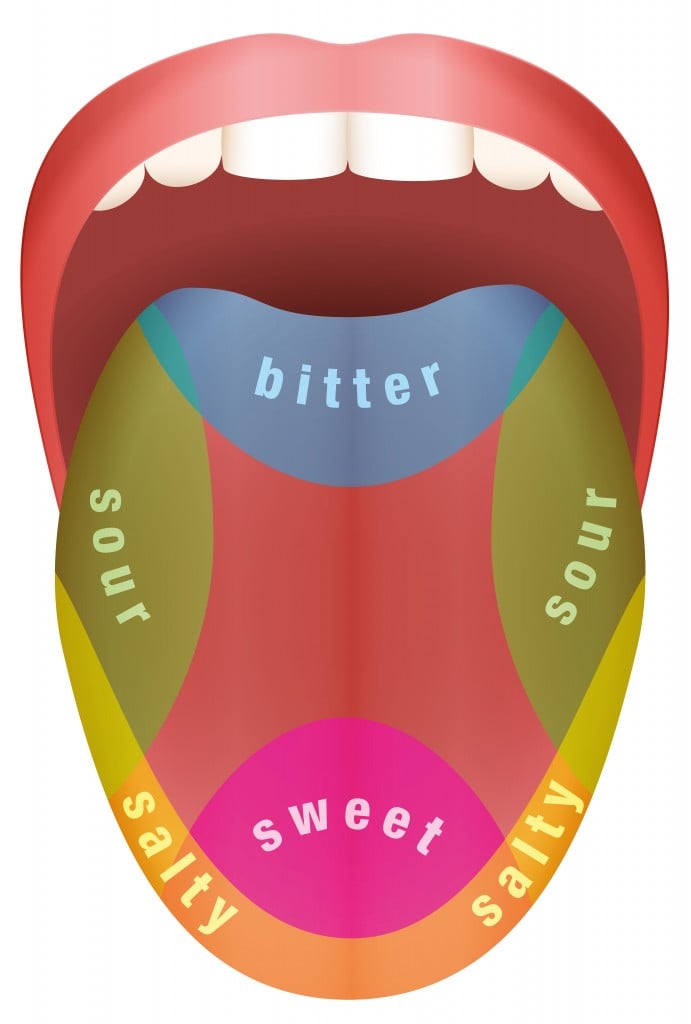
You may have seen a tongue map before, which shows which parts of the tongue are responsible for detecting each taste. However, this map is actually a myth. While certain areas of the tongue may be more sensitive to certain tastes, all parts of the tongue can detect all five basic tastes.
The Taste Buds

Taste buds are clusters of cells on the tongue that detect different flavors. Each taste bud contains 50-100 specialized cells called taste receptor cells, which are responsible for detecting the basic tastes. These cells send signals to the brain, which processes the taste and identifies it.
The Papillae

Papillae are small bumps on the tongue that contain taste buds. There are four types of papillae: fungiform, foliate, circumvallate, and filiform. Fungiform papillae are located at the front of the tongue and are responsible for detecting sweet, sour, and salty tastes. Foliate papillae are located on the sides of the tongue and are responsible for detecting sour tastes. Circumvallate papillae are located at the back of the tongue and are responsible for detecting bitter tastes. Filiform papillae do not contain taste buds and are responsible for detecting texture and temperature.
The Sweet Taste
The sweet taste is detected by taste buds on the tip of the tongue, as well as on the sides of the tongue. The sensitivity to sweetness varies from person to person, but in general, children are more sensitive to sweetness than adults.
The Salty Taste

The salty taste is detected by taste buds on the front and sides of the tongue. Sodium is essential for the body, but too much salt can lead to health problems such as high blood pressure.
The Sour Taste
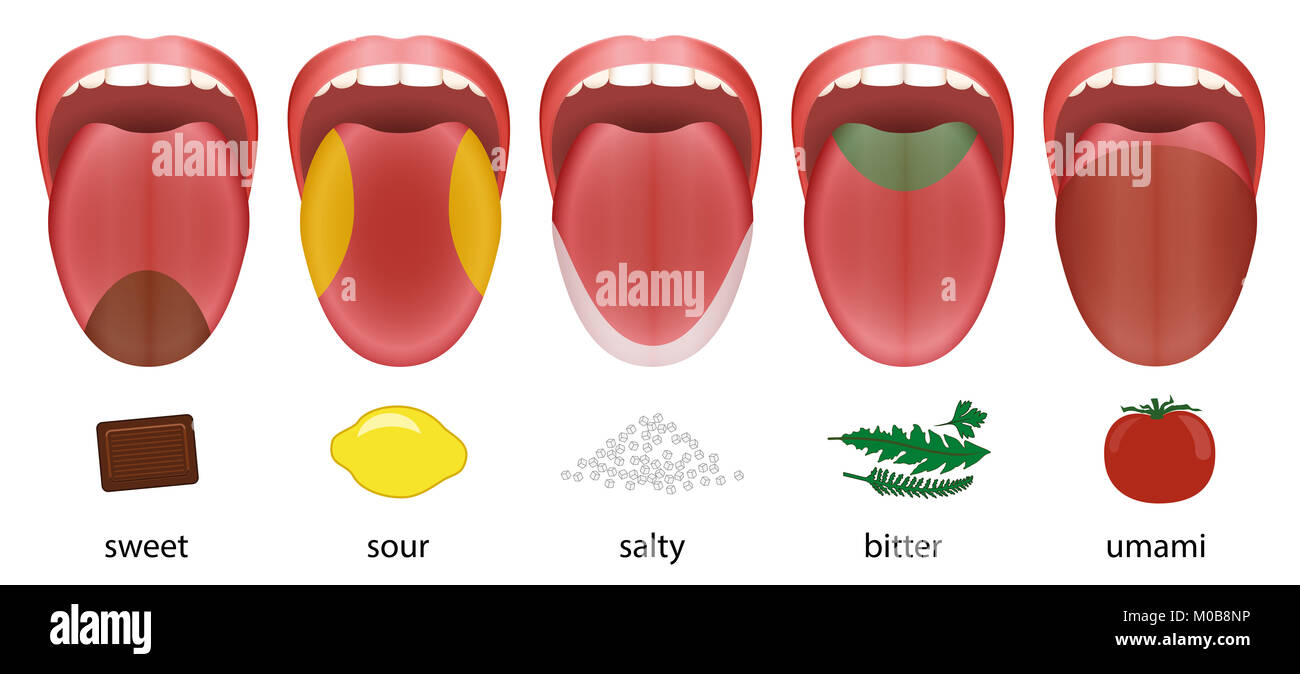
The sour taste is detected by taste buds on the sides of the tongue. Sour foods are often acidic, such as citrus fruits and vinegar. Too much sourness can be unpleasant, but small amounts can add a refreshing tang to food.
The Bitter Taste

The bitter taste is detected by taste buds on the back of the tongue. Bitterness can indicate the presence of toxins in food, which is why humans have evolved to be sensitive to it.
The Umami Taste
The umami taste is detected by taste buds on the front of the tongue. Umami is often described as a savory or meaty taste, and is found in foods such as meat, cheese, and mushrooms.
Taste and Smell

Taste and smell are closely linked, which is why food can taste different when you have a cold or blocked nose. When you eat, odor molecules from the food travel up to the nose, where they are detected by olfactory receptor cells. These cells send signals to the brain, which combines the taste and smell information to create the overall flavor of the food.
The Importance of Taste

Taste is not just about enjoying food – it is also essential for survival. The ability to detect bitter tastes, for example, helps us avoid poisonous plants and animals. Taste also plays a role in digestion, as it triggers the release of digestive enzymes.
Taste Disorders

Some people may experience taste disorders, which can affect their ability to taste food. These disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, such as medication, radiation therapy, or nerve damage. Some people may also be born with a reduced ability to taste certain flavors.
Conclusion
The tongue is a complex and fascinating organ that plays a crucial role in our ability to taste and enjoy food. While each part of the tongue can detect all five basic tastes, different parts may be more sensitive to certain tastes. Understanding how taste works can help us appreciate and enjoy food even more.