Breathing is one of the most vital functions of the human body. It is essential for the proper functioning of the body and its organs. Breathing allows us to inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that is produced in our body as a result of various metabolic processes. Carbon dioxide levels in the blood play a crucial role in our breathing process. In this article, we will discuss how carbon dioxide levels in blood affect breathing.
What is Carbon Dioxide?

Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas that is naturally present in the atmosphere. It is produced in our body as a result of the breakdown of glucose and other nutrients during the metabolic process. Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood to the lungs, where it is exhaled out of the body.
How Does Breathing Work?
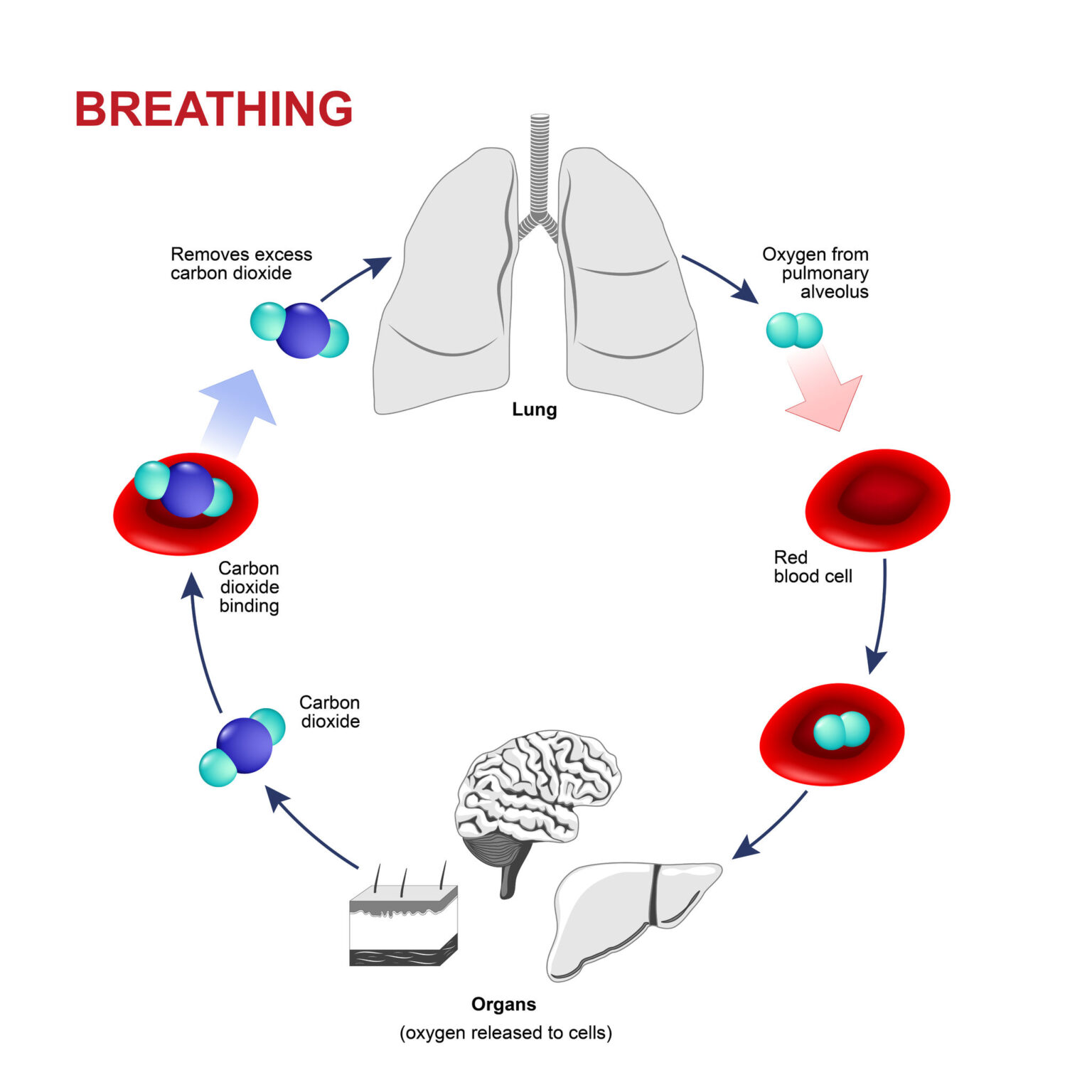
Breathing is a complex process that involves the coordination of various muscles and organs. The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. The process of breathing involves two main steps: inhalation and exhalation. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, and the chest expands, which creates a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes, and the chest contracts, which pushes air out of the lungs.
How Does Carbon Dioxide Affect Breathing?

Carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in the regulation of breathing. When the carbon dioxide levels in the blood are high, it signals the brain to increase the rate and depth of breathing to get rid of the excess carbon dioxide. When the carbon dioxide levels in the blood are low, it signals the brain to decrease the rate and depth of breathing to conserve carbon dioxide.
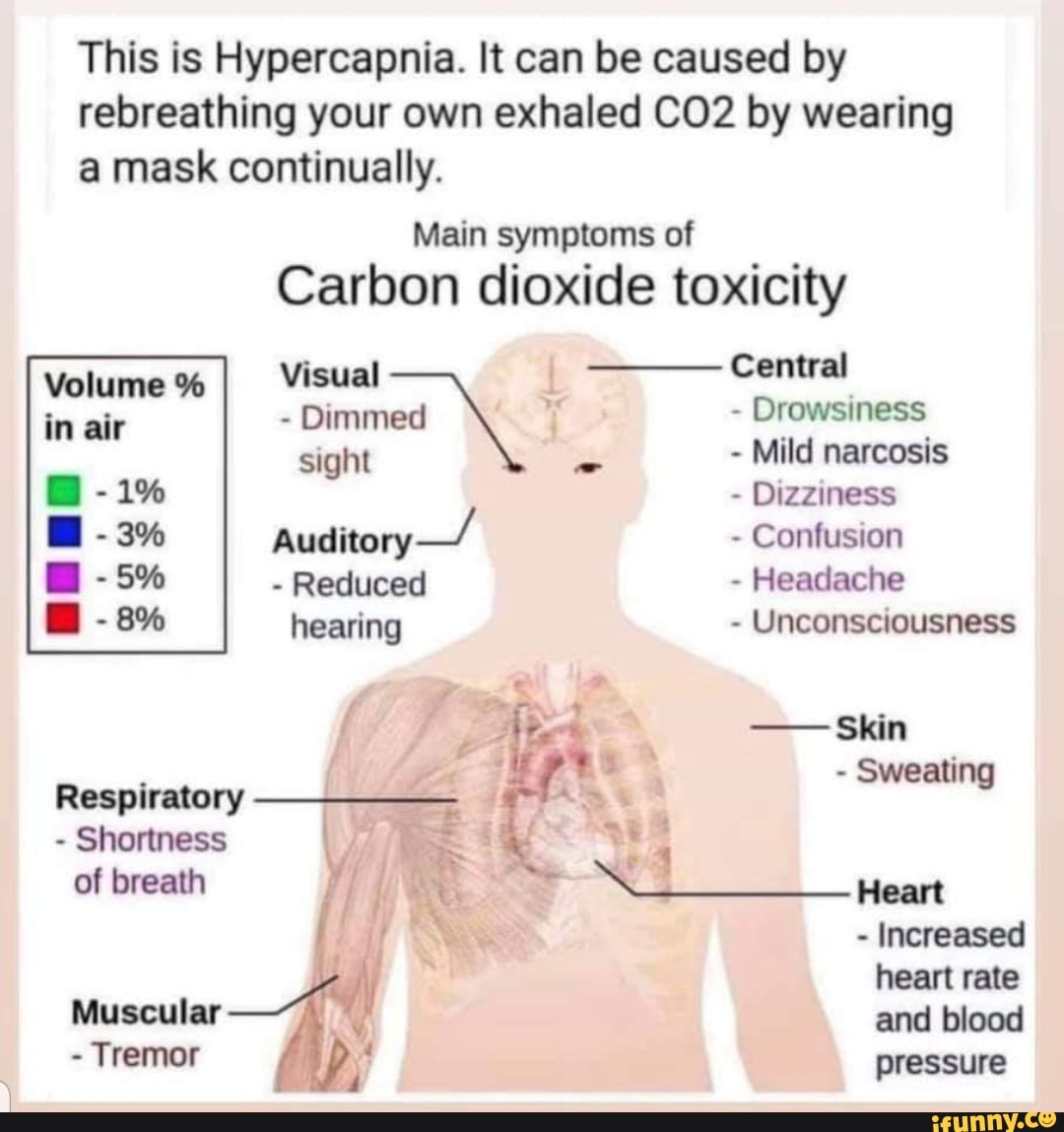
What Happens When Carbon Dioxide Levels are Too High?
When the carbon dioxide levels in the blood are too high, it can lead to a condition called hypercapnia. Hypercapnia can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, confusion, and headaches. In severe cases, it can lead to respiratory failure and death.
What Happens When Carbon Dioxide Levels are Too Low?
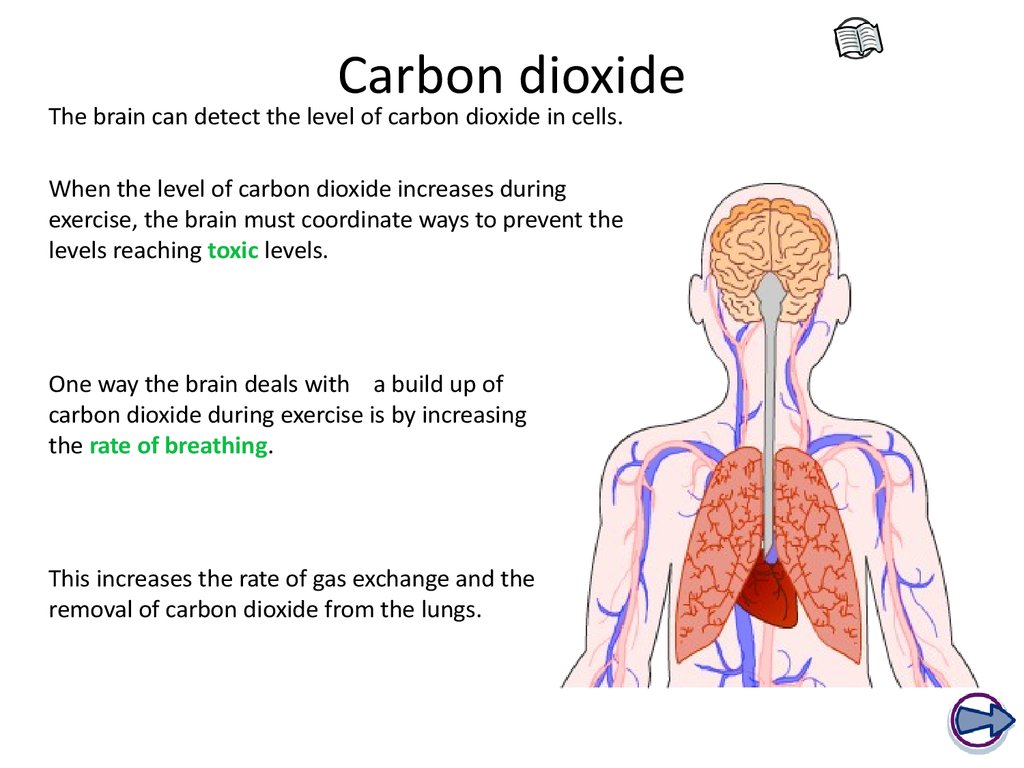
When the carbon dioxide levels in the blood are too low, it can lead to a condition called hypocapnia. Hypocapnia can cause symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and confusion. In severe cases, it can lead to seizures and loss of consciousness.
What Causes Changes in Carbon Dioxide Levels?

Changes in carbon dioxide levels can be caused by various factors such as respiratory disorders, metabolic disorders, and environmental factors. Respiratory disorders such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can cause an increase in carbon dioxide levels. Metabolic disorders such as diabetes and kidney disease can cause a decrease in carbon dioxide levels. Environmental factors such as altitude and air pollution can also affect carbon dioxide levels.
How Can Carbon Dioxide Levels be Monitored?

Carbon dioxide levels can be monitored using various methods such as arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis and capnography. ABG analysis involves taking a sample of arterial blood and measuring the levels of carbon dioxide and other gases. Capnography involves measuring the level of carbon dioxide in exhaled air using a device called a capnometer.
Conclusion
Carbon dioxide levels in the blood play a crucial role in our breathing process. Changes in carbon dioxide levels can lead to various respiratory and metabolic disorders. It is essential to monitor carbon dioxide levels to ensure proper breathing and overall health.